Welcome to HTopo2MMR!!!!
The HTopo2MMR is a structural repository for the 3D structures of human topoiosmerase IIα (hTopoIIα) in complex with various inhibitors at the multitude of binding sites available in the enzyme. This repository also contains the molecular and pharmacodynamic information regarding the various anti-hTopoIIα agents reported in literature. It is a complete repository for the molecular modeling studies on hTopoIIα, and can positively add to the structural understanding of the enzyme so as to facilitate the monitored hTopoIIα inhibitor design.
The human Topoisomerase II (hTopoII) is an enzyme involved in maintaining the DNA topology during replication process. Currently, around 50% of the cancer regimens contain at least one drug that targets Human Topoisomerase II enzyme. The hTopoIIα isoform is abundantly present in rapidly proliferating cells such as cancerous growth. Therefore, targeting hTopoIIα has been considered as an important anticancer treatment strategy. Due to a multistep catalytic cycle (see Figure for details), this enzyme offers a repertoire of checkpoints. In simple words, the hTopoIIα, similar to the other isoform hTopoIIβ, consists of a multitude of inhibitor-binding sites, which are located in the various structural domain of the enzyme. The identification of isoform selective inhibitors indicates the structural differences between the two isoforms. The crystallographic information on the etoposide-binding site and intercalator-binding site is available for hTopoIIβ. The unavailability of the molecular level details of interaction between hTopoIIα and various inhibitors targeting this enzyme raises the need to delineate the structural aspects of this isoform and mechanism of enzyme inhibition by various small molecules. The crystal structure for cleavage complex of hTopoIIα is available in the form of biological assembly, which represents a C-gate open conformation of the enzyme complexed with cleaved G-segment DNA. This structure is not suitable for the understanding of molecular level details of interactions between hTopoIIα and its inhibitors. This raises a need to employ the molecular modeling techniques for extracting the atomic level details molecular recognition interactions at various binding sites in hTopoIIα
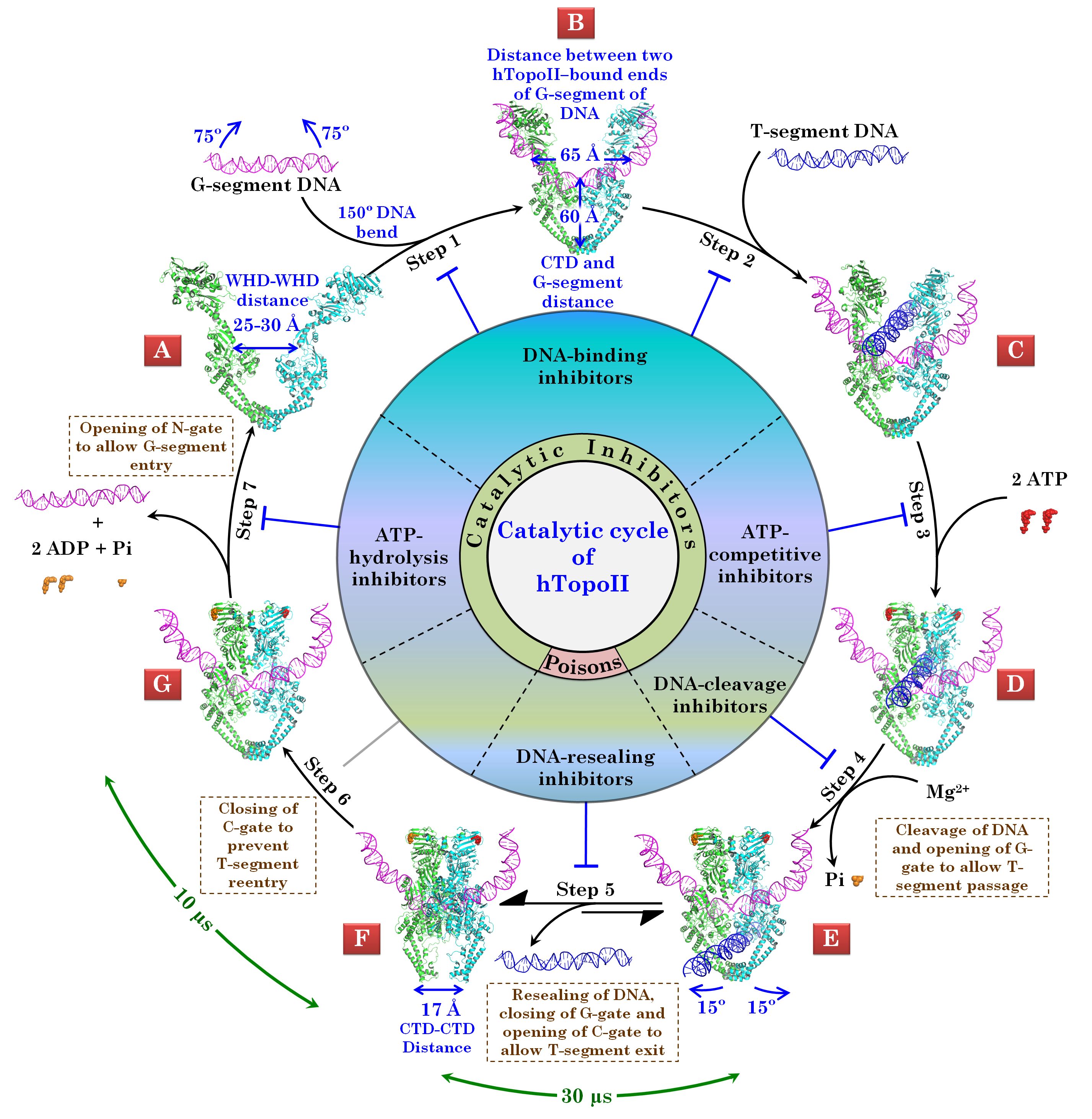
Image reproduced from Tripathi, N. et al. Chapter 2, Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: 2017; pp 49-142.
